Cost Performance Index (CPI): CPI is used to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of a project. For example, if the budget to manufacture 20 keyboards is $5,000, but the actual expenditure is $5,600, the CPI is 0.89. This means for every dollar spent, the project achieves a value of $0.89.
Cost Variance (CV): CV shows the data in actual dollar amounts, not percentages. For example, the cost variance for manufacturing 20 keyboards is -$300.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI): SPI is used to measure whether a project is strictly following the schedule. For example, if the Planned Value (PV) is $5,000 and the Earned Value (EV) is $4,300, the SPI is 0.86.
Schedule Variance (SV): SV is used to indicate whether a project is following the planned timeline. For example, if the EV is $4,300 and the PV is $5,000, the SV is -$700, indicating the project is behind schedule.
Planned Hours vs. Actual Time Spent: This KPI compares the actual time spent with the project manager's initial time estimates. For example, if the planned hours are 100 and the actual time spent is 120, the result is -20 hours, indicating the project is delayed.
Cycle Time: Cycle time is used to measure the time it takes to complete a task. For example, if the cycle time for a task is 5 days, but it actually took 7 days, the project is delayed.
Description
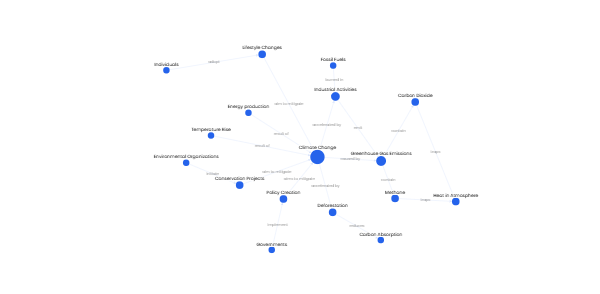
# Gantt Chart for KPI Tracking in Project Management
## Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
* **Cost Performance Index (CPI)**: Assesses a project's cost - effectiveness. If manufacturing 20 keyboards has a budget of $5,000 but actual spending reaches $5,600, CPI = 5,000/5,600 = 0.89. This means each dollar spent generates $0.89 of value.
* **Cost Variance (CV)**: Reflects cost differences in actual dollars. For the keyboard example, CV = 5,000 - 5,600 = - $600, indicating the project is over budget.
* **Schedule Performance Index (SPI)**: Determines if the project is on schedule. With a Planned Value (PV) of $5,000 and an Earned Value (EV) of $4,300, SPI = 4,300/5,000 = 0.86, suggesting schedule delays.
* **Schedule Variance (SV)**: Indicates schedule adherence. If EV is $4,300 and PV is $5,000, SV = 4,300 - 5,000 = - $700, meaning the project lags behind.
* **Planned Hours vs. Actual Time Spent**: Compares actual time with planned time. If planned hours are 100 but actual hours spent are 120, the difference of - 20 hours shows a project delay.
* **Cycle Time**: Measures task completion time. A task with a planned cycle time of 5 days but actual completion in 7 days indicates a delay.
## Gantt Chart Application
* **Timeline Representation**: The Gantt chart's horizontal axis represents the project timeline, while the vertical axis lists project tasks or activities.
* **Bar Visualization**: Each task is represented by a bar. The length of the bar corresponds to the task's duration. For instance, a task spanning five days will have a longer bar than a three - day task.
* **Progress Indication**: As the project progresses, bars can be shaded or colored to show completion status. A fully shaded bar means the task is complete, while a half - shaded bar indicates 50% completion.
* **KPI Integration**: KPIs like CPI and SPI can be displayed alongside the chart. A CPI of 0.89 and an SPI of 0.86, shown next to relevant tasks, quickly highlight cost and schedule issues.
* **Planned vs. Actual Comparison**: By displaying planned hours and actual time spent, the Gantt chart allows for easy comparison. Bars for actual time can extend beyond planned time bars, visually indicating delays.
* **Cycle Time Monitoring**: The chart can show planned and actual cycle times. If a task's actual cycle time exceeds the planned time, it can be flagged for attention.
## Benefits for Project Management
* **Visual Clarity**: Provides a clear, visual overview of project tasks, timelines, and KPIs, making it easier for project managers and team members to understand the project's status at a glance.
* **Early Issue Detection**: Helps identify potential cost overruns and schedule delays early by tracking KPIs. For example, a negative CV or SV alerts the team to take corrective action promptly.
* **Resource Allocation**: Assists in optimizing resource allocation. By monitoring KPIs like CPI, managers can reallocate resources to cost - efficient tasks if needed.
* **Progress Reporting**: Simplifies progress reporting to stakeholders. The Gantt chart offers a comprehensive view of the project's progress, making it easier to communicate achievements and challenges.
* **Decision - Making Support**: Offers data - driven insights to support decision - making. Project managers can use KPI trends to make informed decisions about project adjustments and improvements.
* **Team Coordination**: Enhances team coordination by providing a shared visual reference. Team members can see how their tasks fit into the overall project timeline and adjust their work accordingly.