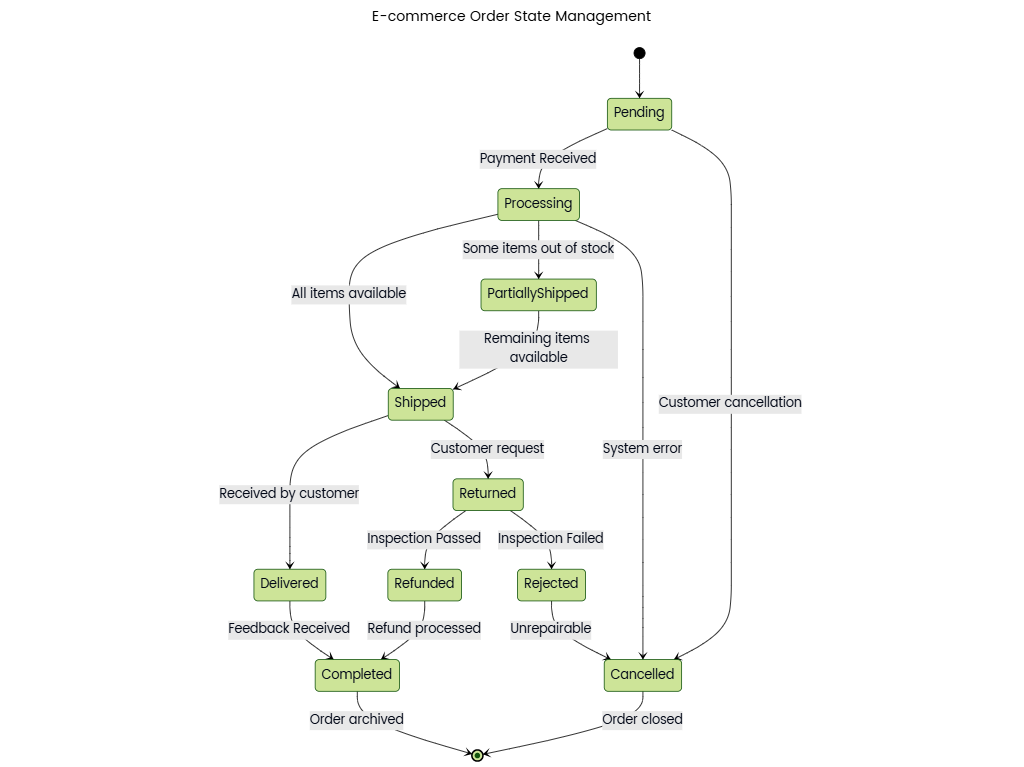
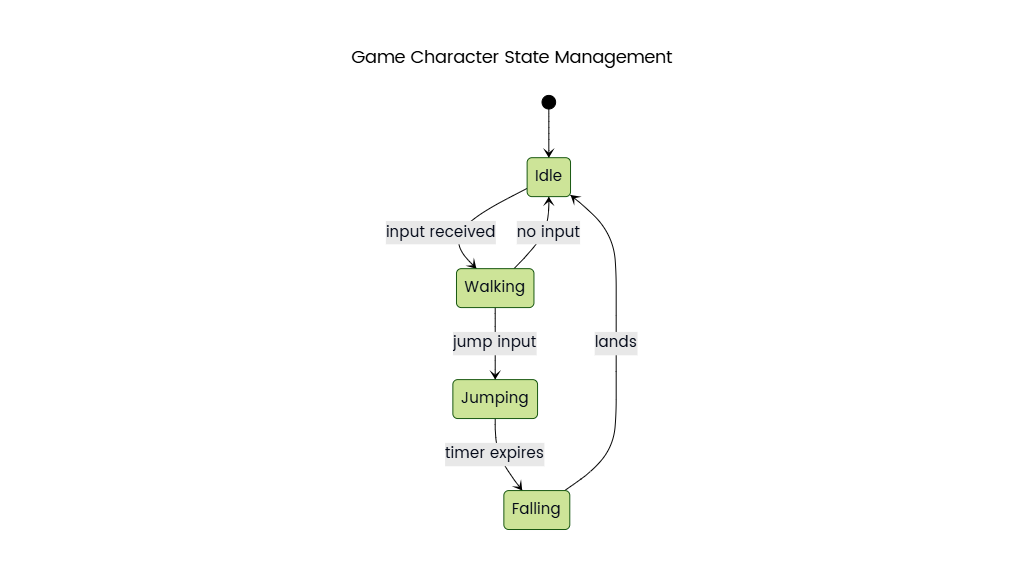
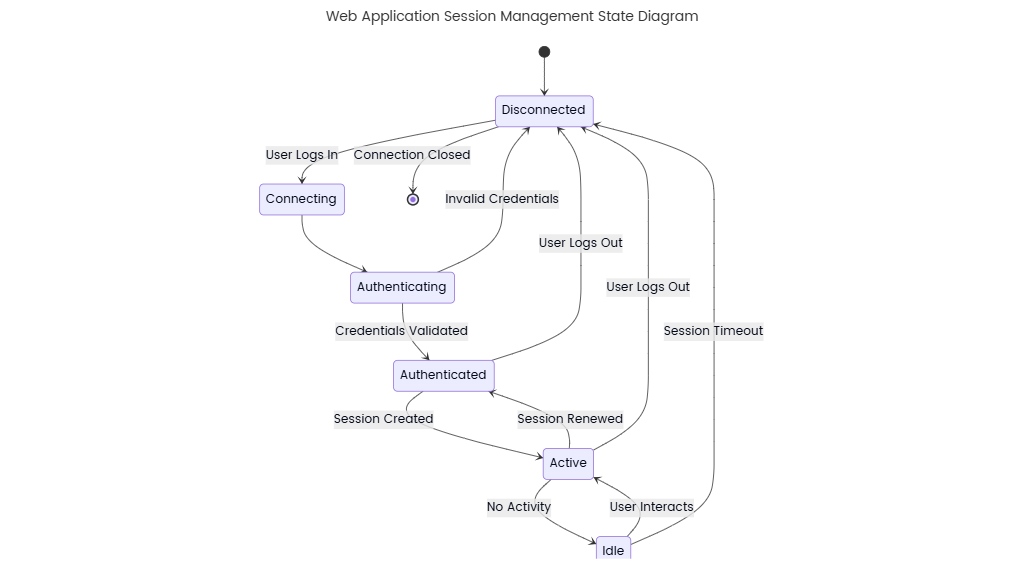
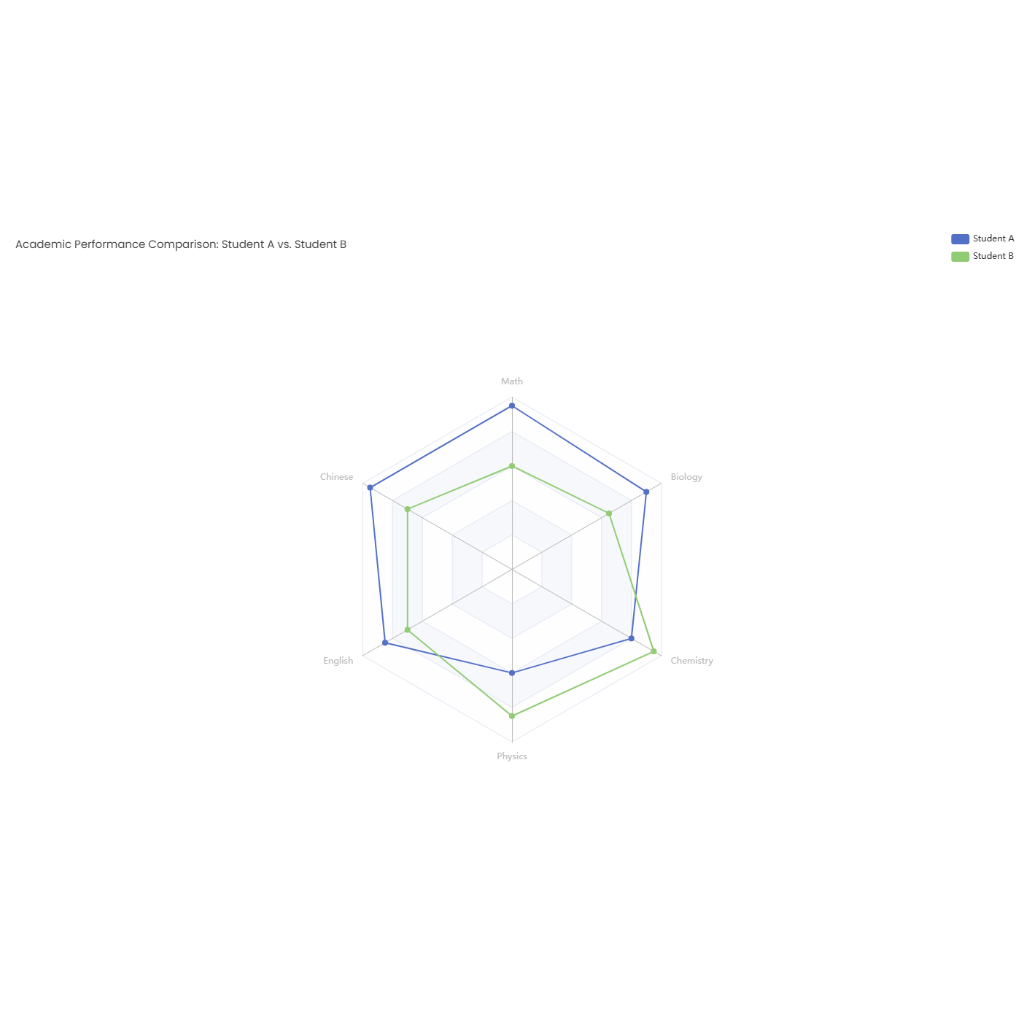
Climate change is driven by several factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and industrial activities. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise. Deforestation reduces the Earth's ability to absorb carbon dioxide, further accelerating climate change. Industrial activities, especially burning fossil fuels, contribute heavily to emissions. Governments, environmental organizations, and individuals take actions like policy creation, conservation projects, and lifestyle changes to mitigate climate change.
Entities and Types:
Climate Change — Concept
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — Concept
Deforestation — Concept
Industrial Activities — Concept
Carbon Dioxide — Chemical Compound
Methane — Chemical Compound
Global Temperature Rise — Effect
Governments — Organization
Environmental Organizations — Organization
Individuals — Person
Policy Creation — Action
Conservation Projects — Action
Lifestyle Changes — Action
Fossil Fuels — Resource
Relationships (ensuring all entities are connected):
Climate Change — caused by — Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Climate Change — accelerated by — Deforestation
Climate Change — accelerated by — Industrial Activities
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — contain — Carbon Dioxide
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — contain — Methane
Carbon Dioxide — traps — Heat in Atmosphere
Methane — traps — Heat in Atmosphere
Deforestation — reduces — Carbon Absorption
Fossil Fuels — burned in — Industrial Activities
Industrial Activities — emit — Greenhouse Gases
Global Temperature Rise — result of — Climate Change
Governments — implement — Policy Creation
Environmental Organizations — initiate — Conservation Projects
Individuals — adopt — Lifestyle Changes
Policy Creation — aims to mitigate — Climate Change
Conservation Projects — aim to mitigate — Climate Change
Lifestyle Changes — aim to mitigate — Climate Change
Description
Overview: What Drives Climate Change?
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature, weather patterns, and environmental conditions on Earth. It is primarily driven by human activities, with three major contributing factors:
- Greenhouse gas emissions – These gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and leading to rising global temperatures.
- Deforestation – Trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide. Removing forests reduces this natural absorption capacity, causing more CO₂ to stay in the atmosphere.
- Industrial activities – Manufacturing, transportation, and energy production burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas, significantly increasing greenhouse gas levels.
These actions collectively contribute to a rise in global temperatures, which causes further environmental disruptions such as ice melting, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather events.
Key Concepts and Elements Involved
Several core components are involved in the climate change system:
- Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄), are key players. CO₂ is largely released from burning fossil fuels, while CH₄ comes from agriculture and waste. Both are extremely effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere.
- Deforestation interrupts the carbon cycle by eliminating trees that would otherwise absorb CO₂ from the air.
- Fossil fuels are the primary energy source for industrial activities. When burned, they release massive amounts of greenhouse gases.
- Industrial activities both consume fossil fuels and emit emissions directly, making them a dual contributor.
Relationships Between These Elements
The components are interconnected through cause-effect and role-function relationships. Here's how they relate:
- Climate change is caused by greenhouse gas emissions.
- It is accelerated by both deforestation and industrial activities.
- Greenhouse gas emissions contain both carbon dioxide and methane.
- Carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the atmosphere, contributing directly to warming.
- Deforestation reduces the Earth’s ability to absorb CO₂, intensifying atmospheric buildup.
- Fossil fuels are burned during industrial activities, which in turn emit greenhouse gases.
- The global temperature rise is a direct result of climate change.
Efforts to Mitigate Climate Change
Several groups and strategies are involved in combating climate change:
- Governments play a key role by creating and enforcing policies aimed at reducing emissions and encouraging renewable energy.
- Environmental organizations carry out conservation projects, such as reforestation, wildlife protection, and ecosystem restoration.
- Individuals can contribute by making lifestyle changes, such as using public transport, reducing meat consumption, conserving energy, and supporting sustainable practices.
Each of these actions—policy creation, conservation work, and lifestyle shifts—aims to mitigate the effects of climate change and build a more sustainable future.
Final Thoughts
This structure outlines a systemic view of climate change, where:
- Causes (emissions, deforestation, industry) are identified,
- Key chemical agents (CO₂ and CH₄) are described,
- Effects (global warming) are linked,
- And mitigation efforts (by governments, organizations, and individuals) are emphasized.
It serves as a knowledge graph in text form, great for educational purposes, AI understanding, or structuring climate-related data for apps or analysis.
Let me know if you’d like this visualized as a mind map, diagram, or network!