Added on:
May 08, 2025
User Prompt
C4 Diagrams:Hospital Information System Architecture
Description
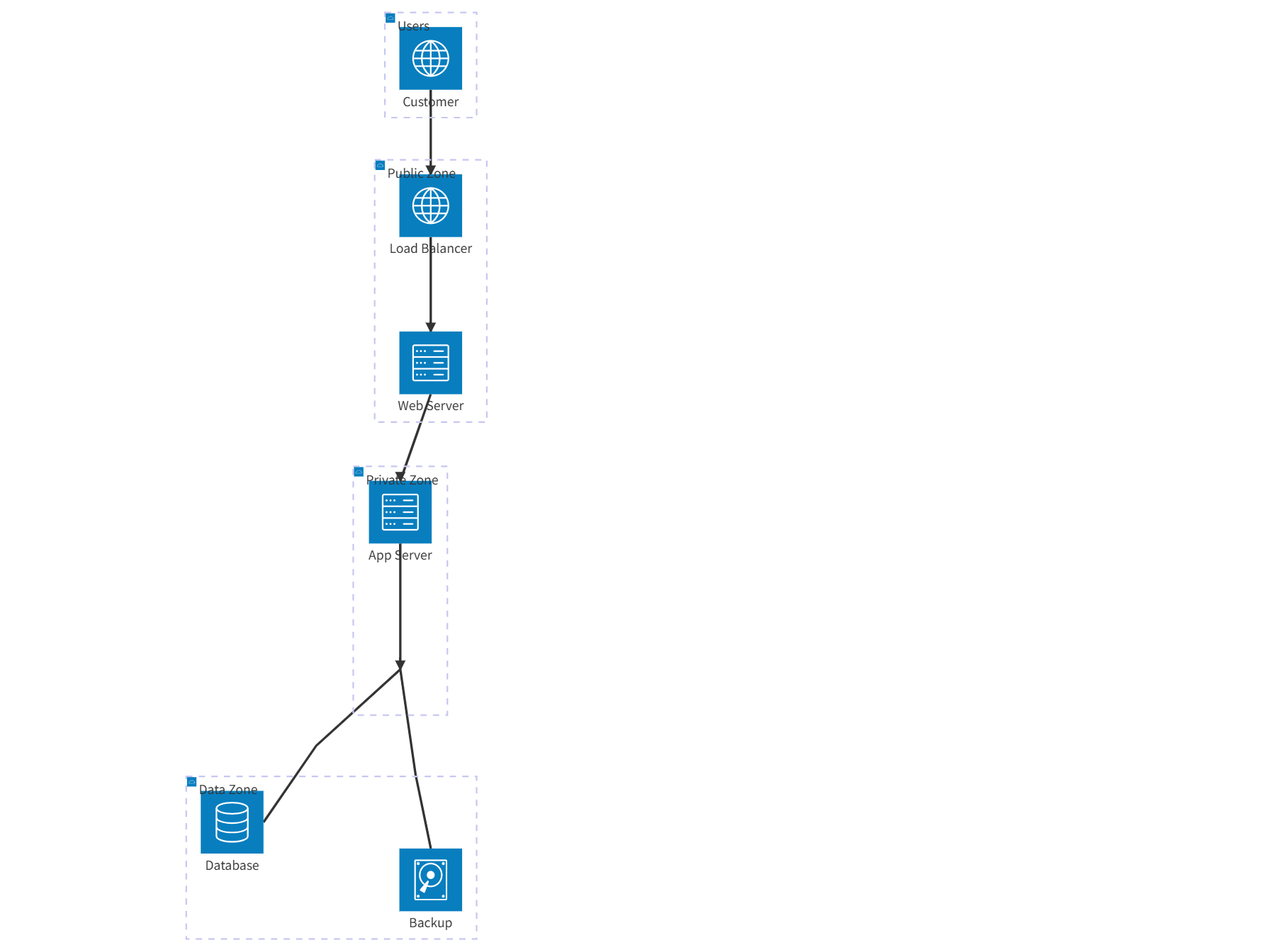
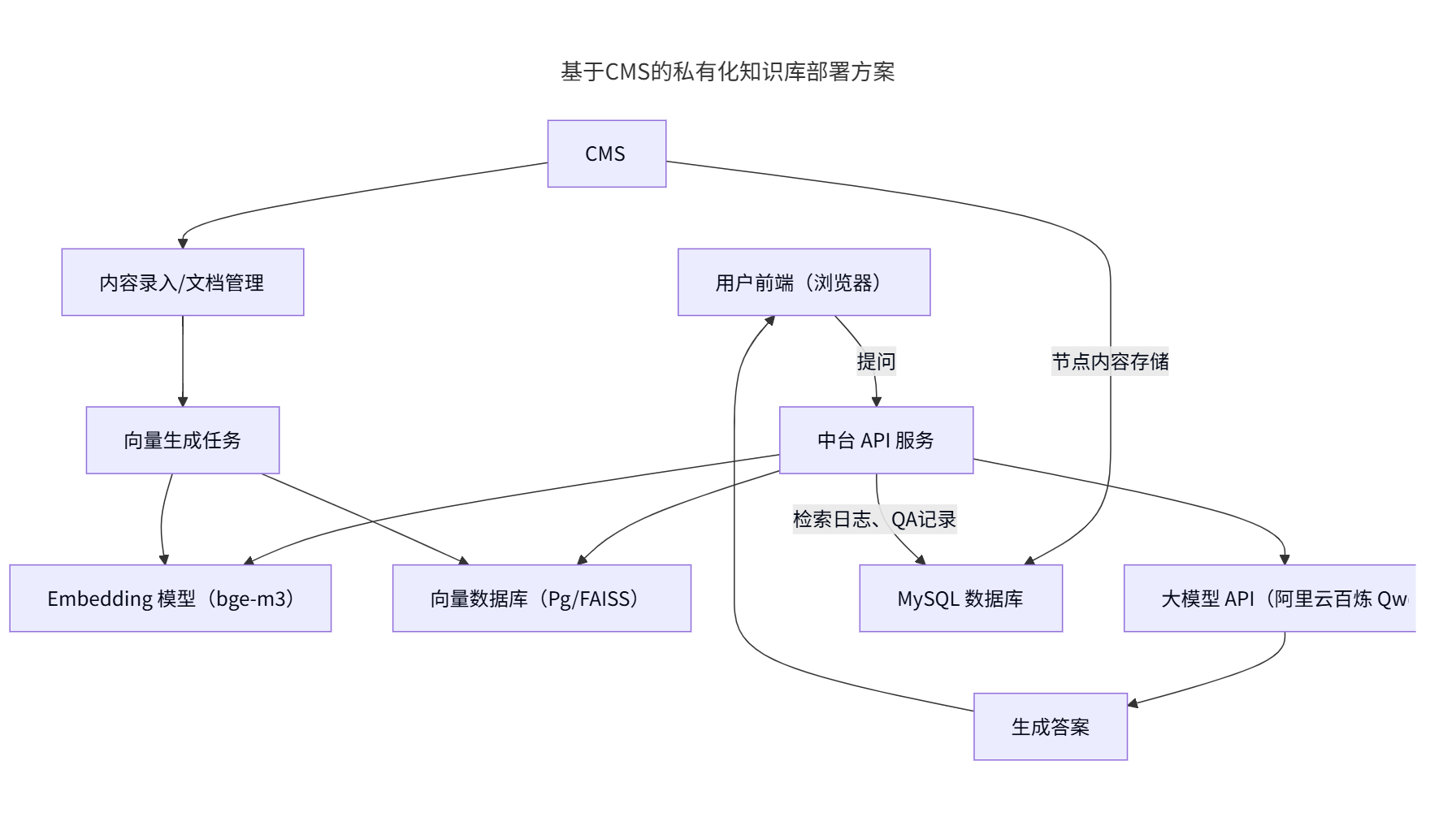
A C4 model for a Hospital Information System (HIS) provides a hierarchical view of the architecture, from high-level context to detailed component interactions. This approach ensures stakeholders understand the system’s scope, relationships, and technical implementation.
1. Context Diagram (Level 1)
- Primary Actors:
- Patients: Access portals for appointments, test results, and billing.
- Clinical Staff: Doctors, nurses, and technicians using EHRs, order entry, and patient monitoring tools.
- Administrative Staff: Manage scheduling, billing, and HR functions.
- External Systems: Integrate with pharmacies, labs, insurance providers, and public health agencies.
- Core System:
- HIS: Centralized platform managing patient records, appointments, clinical workflows, and billing.
2. Container Diagram (Level 2)
- Containers:
- Web Application: Frontend for clinical and administrative users (e.g., React-based portal).
- Mobile App: Patient-facing interface for appointments and health tracking (iOS/Android).
- API Gateway: Routes requests to microservices (e.g., Express.js).
- Microservices:
- EHR Service: Manages patient records, allergies, and treatment history.
- Appointment Service: Handles scheduling and resource allocation.
- Billing Service: Processes insurance claims and patient invoicing.
- Notification Service: Sends alerts (e.g., appointment reminders, lab results).
- Databases:
- Relational DB: Stores structured data (patients, staff, appointments).
- NoSQL DB: Manages unstructured data (clinical notes, images).
- Message Broker: Enables asynchronous communication (e.g., Kafka for lab result updates).
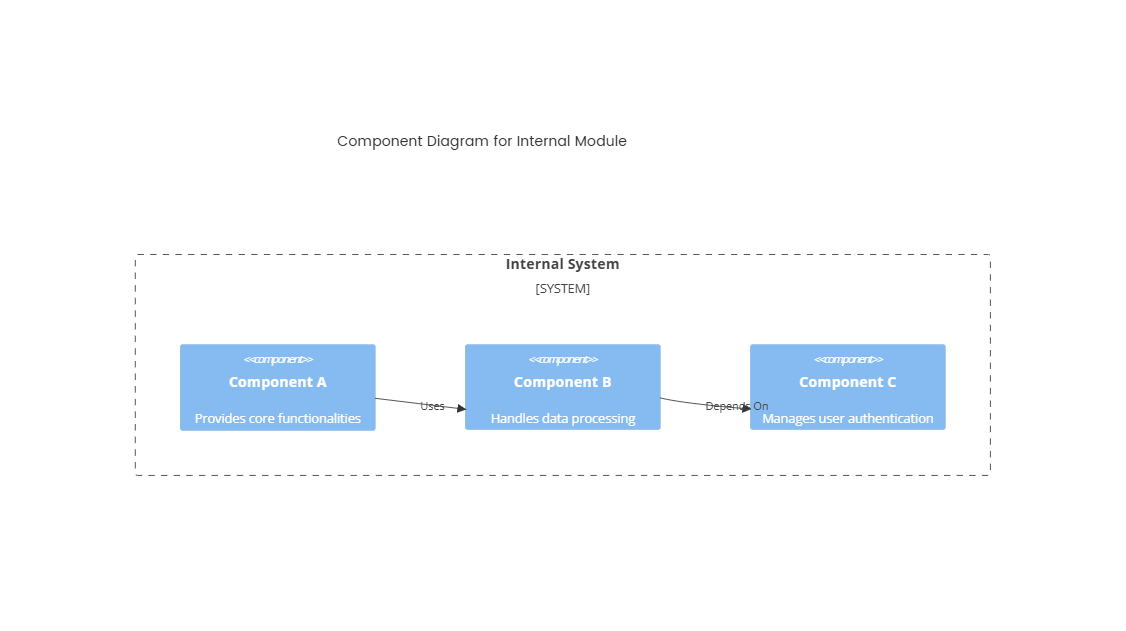
3. Component Diagram (Level 3)
- Components (Example: EHR Service):
- Patient Record Manager: Creates/updates patient profiles.
- Medication Management: Tracks prescriptions and interactions.
- Clinical Decision Support: Provides evidence-based treatment recommendations.
- Audit Logging: Records access and modifications for compliance.
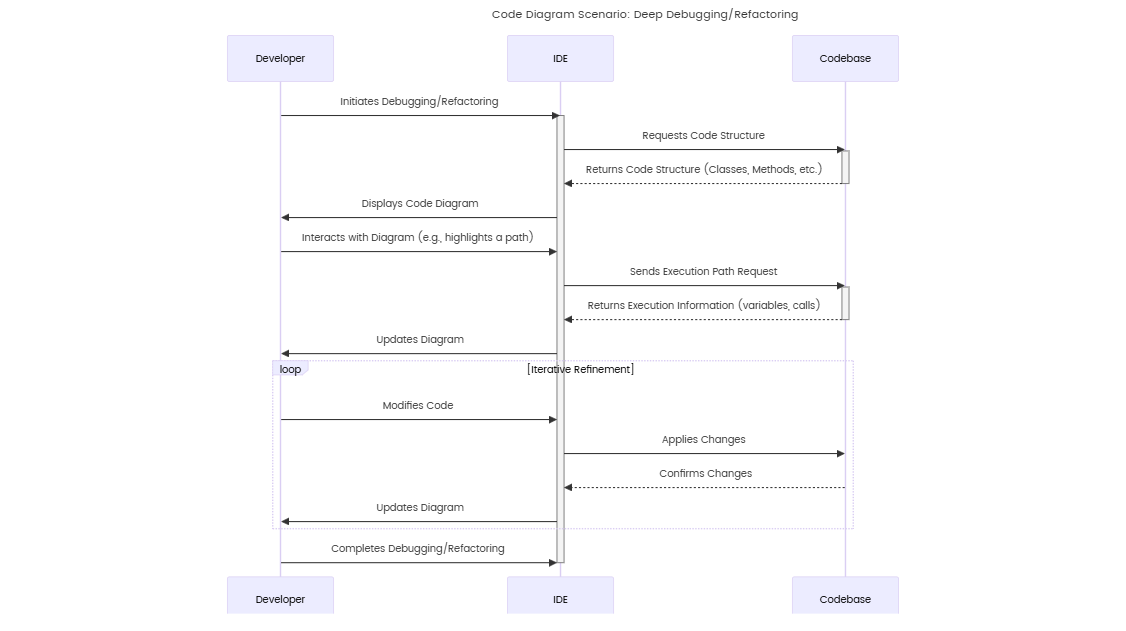
4. Code Diagram (Level 4)
- Technical Details:
- Frameworks: Spring Boot (Java) for backend services, Angular for web UI.
- APIs: RESTful endpoints with OAuth2 authentication.
- Data Storage: PostgreSQL for relational data, MongoDB for documents.
Key Relationships
- Integration Points:
- HIS → Lab Systems: Sends test orders, receives results.
- HIS → Pharmacy Systems: Transmits prescriptions, checks drug availability.
- HIS → Billing Systems: Exchanges insurance eligibility and payment data.
Design Principles
- Security: Role-based access control (RBAC), HIPAA compliance, data encryption.
- Scalability: Microservices architecture allows independent scaling of critical components.
- Resilience: Redundant databases and failover mechanisms ensure continuous operation.