Added on:
May 07, 2025
User Prompt
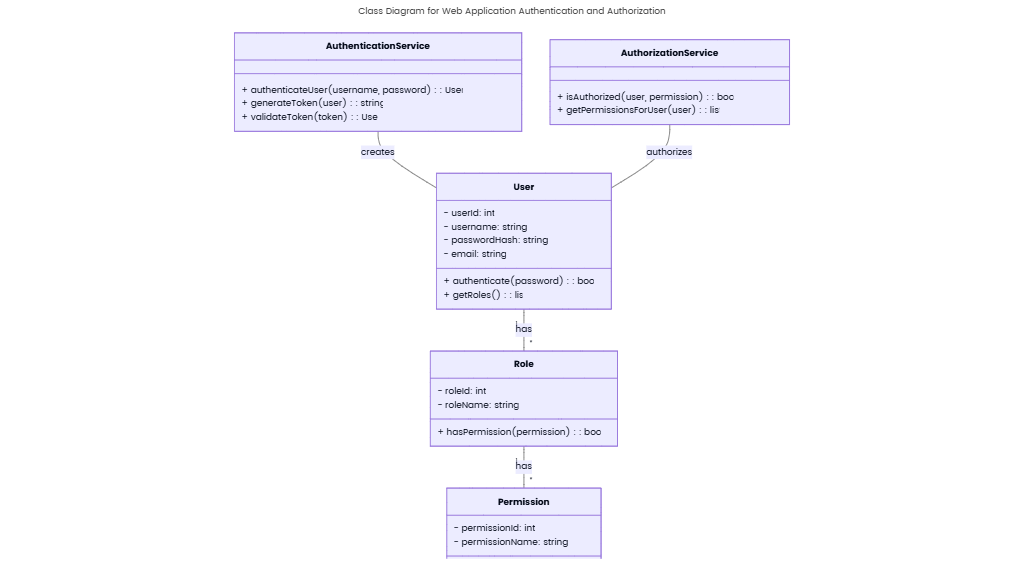
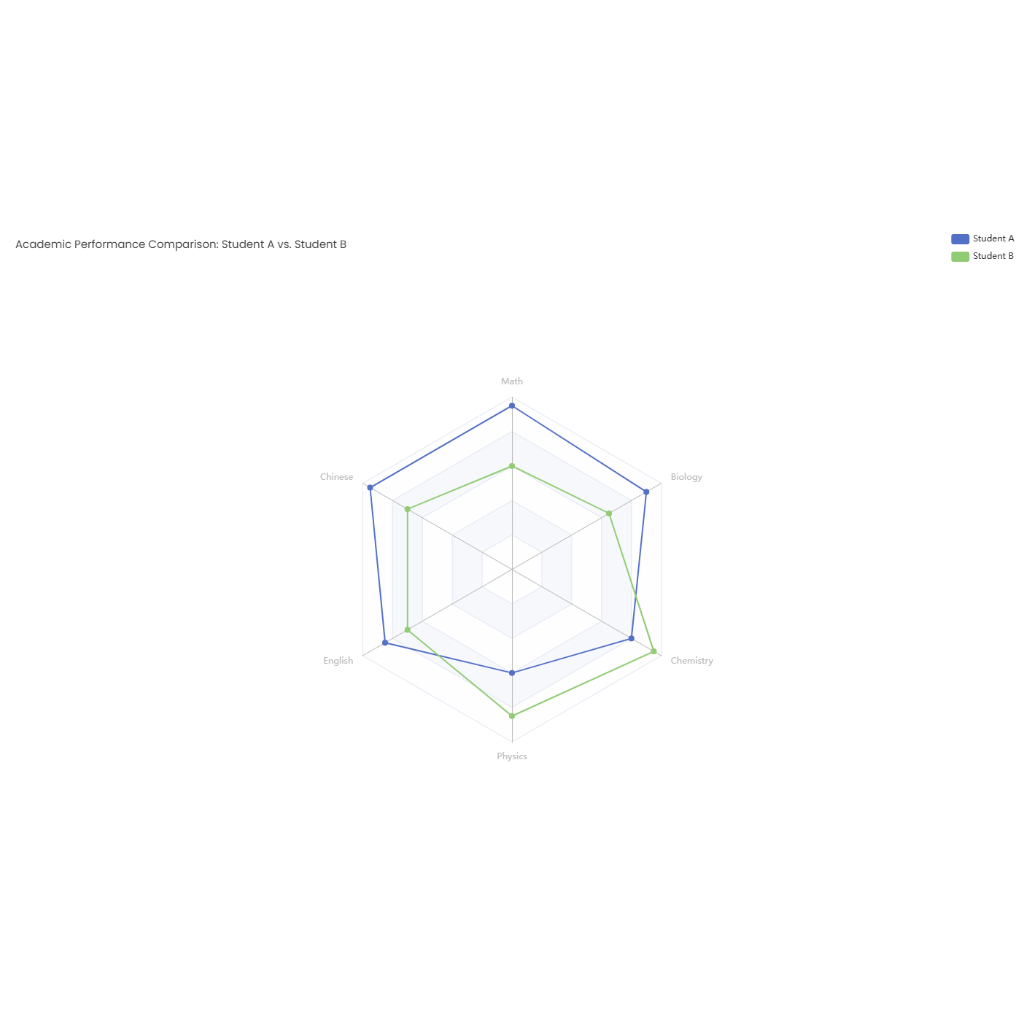
State Diagram for E-commerce Order State Management
Description
A state diagram for e-commerce order management visualizes the lifecycle of an order from creation to fulfillment, ensuring transparency and automation across key stages. This diagram is not same as ER diagram, this diagram models states, transitions, and triggers to streamline operations and enhance customer experience.
Core States
- Created
- Order is initialized but payment is pending.
- Triggers:
- Customer adds items to cart and proceeds to checkout.
- Actions:
- Generate order ID, lock inventory (if applicable).
- Payment Pending
- Awaiting payment confirmation (e.g., processing credit card, PayPal).
- Triggers:
- Customer submits payment information.
- Actions:
- Validate payment details, initiate transaction.
- Paid
- Payment is successful; order moves to processing.
- Triggers:
- Payment gateway confirms transaction.
- Actions:
- Deduct inventory, send order confirmation email.
- Processing
- Order is being prepared for shipment (e.g., picking, packing).
- Triggers:
- System auto-transitions from
Paidor manual verification.
- System auto-transitions from
- Actions:
- Assign warehouse staff, generate packing slip.
- Shipped
- Order is en route to the customer.
- Triggers:
- Warehouse scans package for shipment.
- Actions:
- Update tracking information, notify customer.
- Delivered
- Order is successfully received by the customer.
- Triggers:
- Delivery confirmation (e.g., signature, GPS tracking).
- Actions:
- Mark order complete, release payment to merchants.
- Cancelled
- Order is terminated before fulfillment.
- Triggers:
- Customer request, payment failure, or stock unavailability.
- Actions:
- Refund payment (if applicable), restock items.
- Returned
- Customer returns the order post-delivery.
- Triggers:
- Customer initiates return process.
- Actions:
- Process refund, inspect returned items, restock if valid.
Key Transitions & Triggers
- Payment Failure
- Transition:
Payment Pending→Cancelled. - Trigger: Transaction declines (e.g., insufficient funds).
- Action: Notify customer, unlock inventory.
- Transition:
- Inventory Check
- Transition:
Paid→Processing(if in stock) orOn Hold(if backordered). - Trigger: System verifies stock levels.
- Action: Allocate items or notify customer of delay.
- Transition:
- Expedited Fulfillment
- Transition:
Processing→Shippedbypassing standard queues. - Trigger: Premium shipping option selected.
- Action: Prioritize order in warehouse.
- Transition:
- Return Approval
- Transition:
Delivered→Return Pending→Returned. - Trigger: Customer request + merchant approval.
- Action: Issue return label, update inventory on receipt.
- Transition:
- Partial Fulfillment
- Transition:
Processing→Shipped(for available items) +Backordered(for missing items). - Trigger: Some items are out of stock.
- Action: Ship available items, notify customer of backorder.
- Transition:
Design Considerations
- Automation:
- Use webhooks (e.g., payment gateway notifications) to trigger state changes.
- Example: Stripe integration auto-updates from
Payment PendingtoPaid.
- User Communication:
- Send automated emails/SMS for state transitions (e.g., "Your order is shipped!").
- Edge Cases:
- Handle scenarios like fraud detection (
Paid→On Hold). - Implement timeout logic for
Payment Pending(e.g., cancel after 24 hours).
- Handle scenarios like fraud detection (
- Integration:
- Connect with inventory management systems to reflect real-time stock changes.
- Reporting:
- Track metrics like average time from
CreatedtoShippedfor operational efficiency.
- Track metrics like average time from