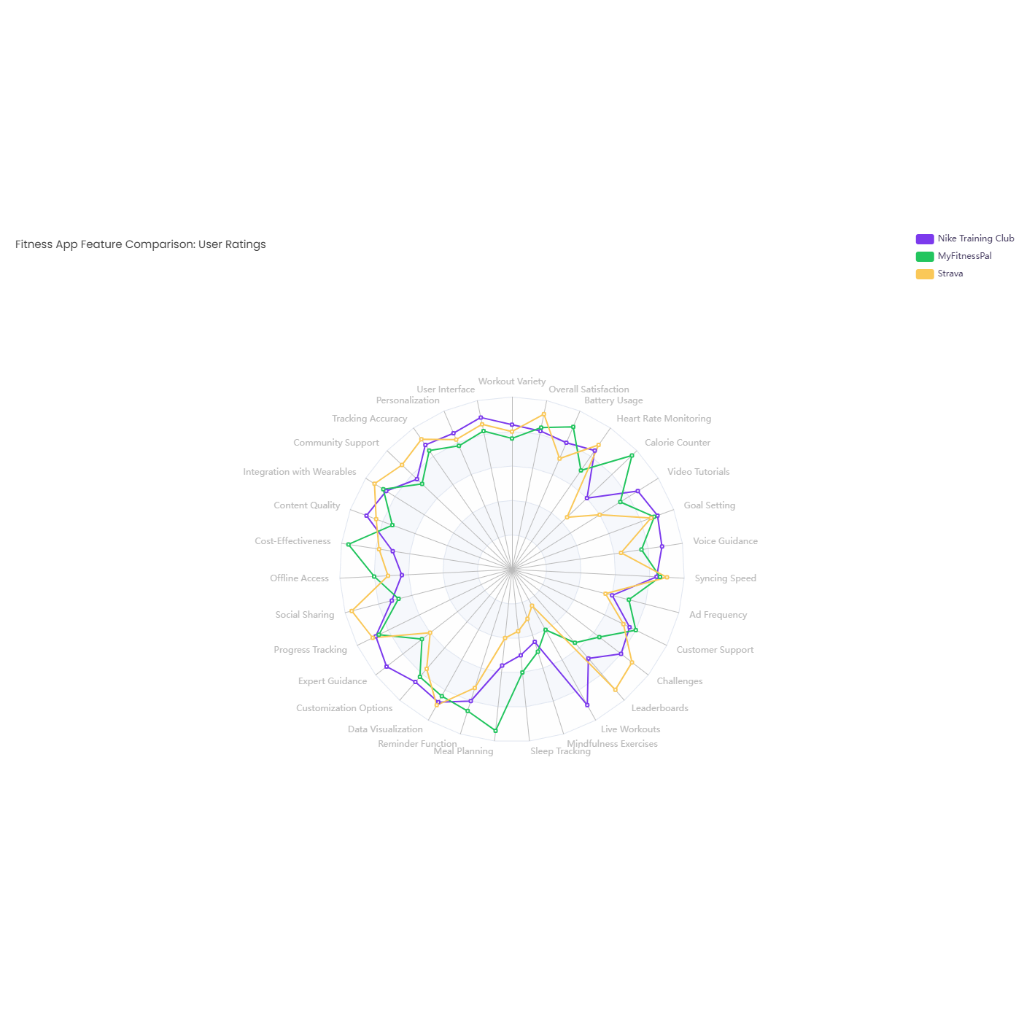
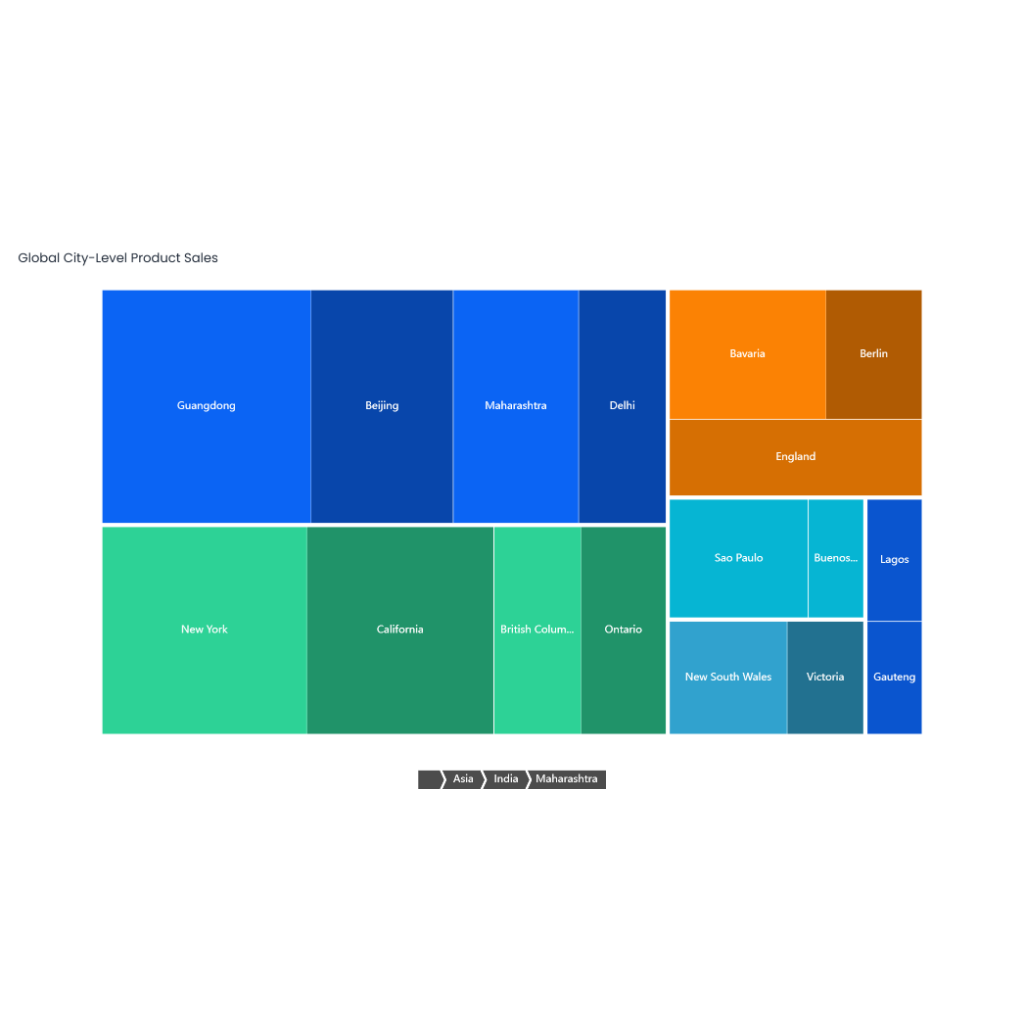
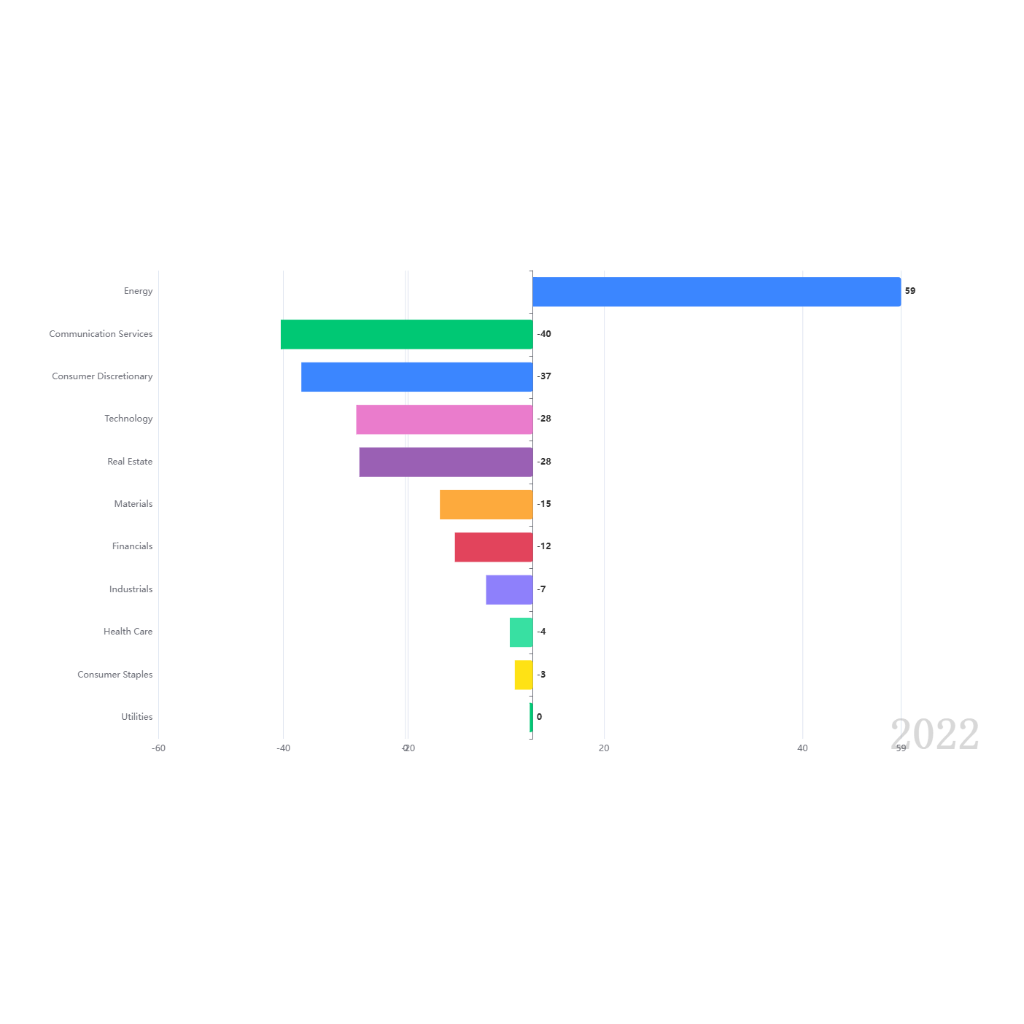
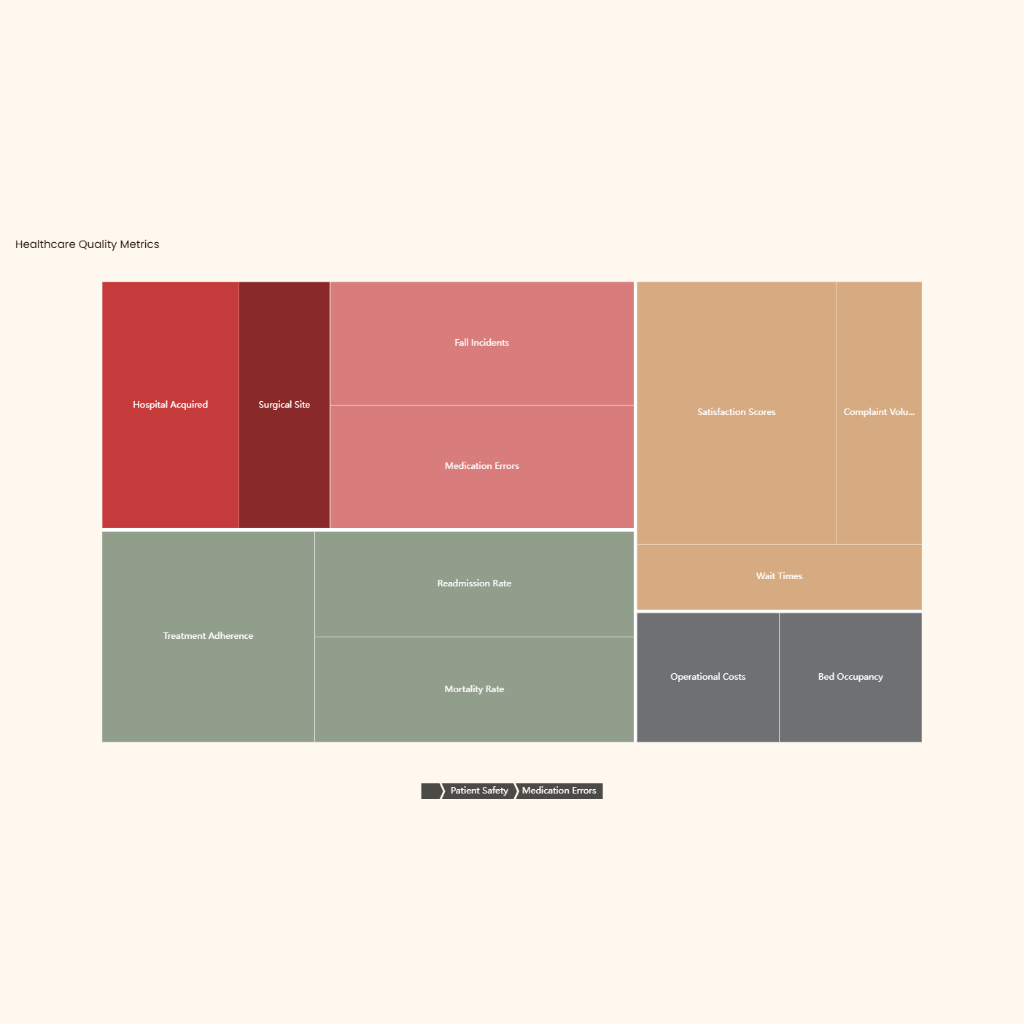
- Problem/Issue: Medication errors are common, contributing to adverse drug events and patient harm.
- Focus: Inpatient wards where there is the highest proportion of drug administration.
- Project Objective: A 40% reduction of medication errors in six months.
- Existing process: Medication orders are transcribed manually and there is only partial use of the electronic prescribing system.
- Root Cause Analysis: Causes of error include transcription errors, non-uniform protocols, and inadequately trained staff.
- State of evidence: Audits indicate a high level of variations between medicines that are ordered and taken.
- Strategies/Improvement Theories:
- Hospitals should adopt electronic prescription and medicine administration.
- Standardize medication administration protocols.
- Schedule routine training for all staff on safe medication practices.
- Response to the Problem:
- Switch to an electronic prescribing system in order to reduce transcription errors.
- Develop and disseminate standardized treatment protocols for medical countermeasures.
- Arrange for nursing and pharmacy staff to participate in monthly training workshops.
- Rapid Cycle Improvements, Details of Testing:
- Implement the electronic system in one ward prior to hospital roll-out.
- Solicit staff feedback on clarity of protocol and effectiveness of training.
Study
- Analysis of Testing:
- Monitor error ratios for weekly audits after the change has gone live.
- Assess staff skills and confidence with new systems and protocols.
- Observations Deviation from Expectation:
- A 25% fall in errors has been recorded in initial figures for the first three months of the service with staff praising the ease of electronic systems.