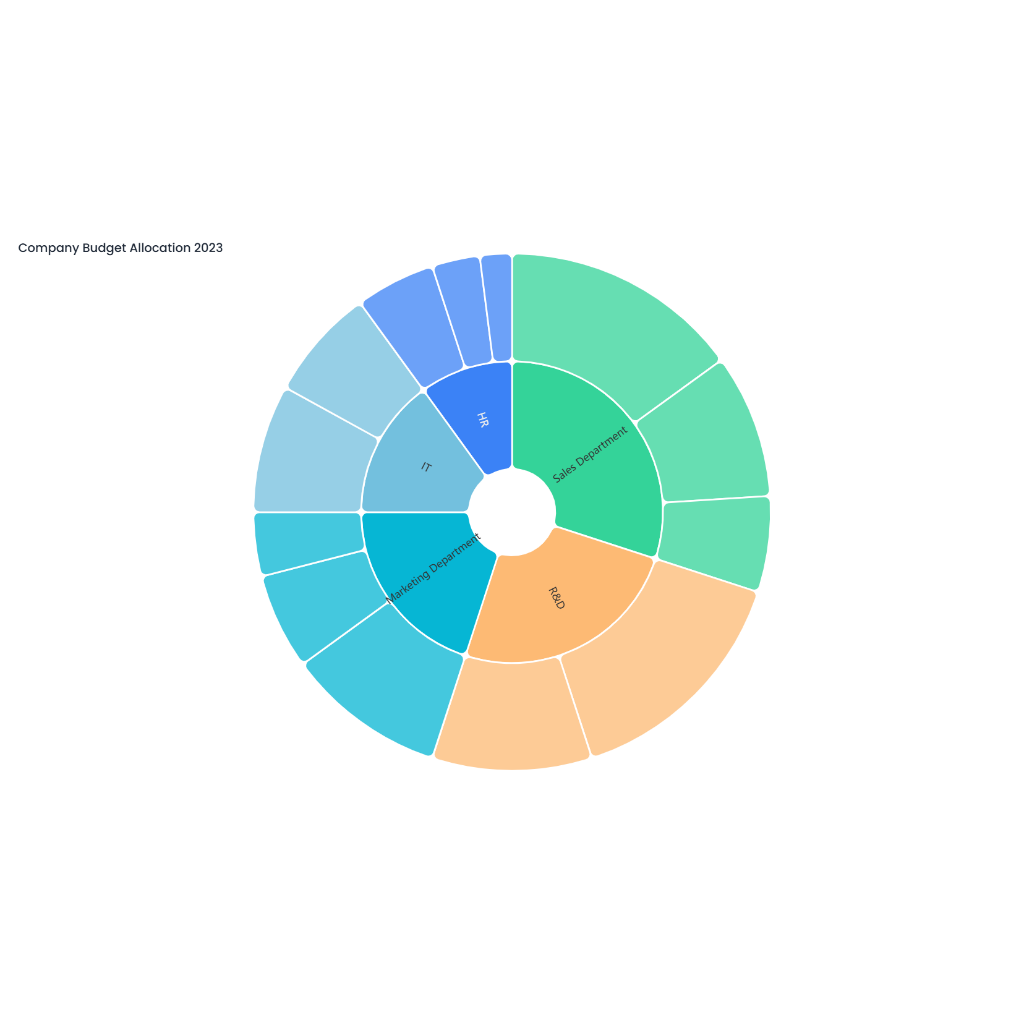
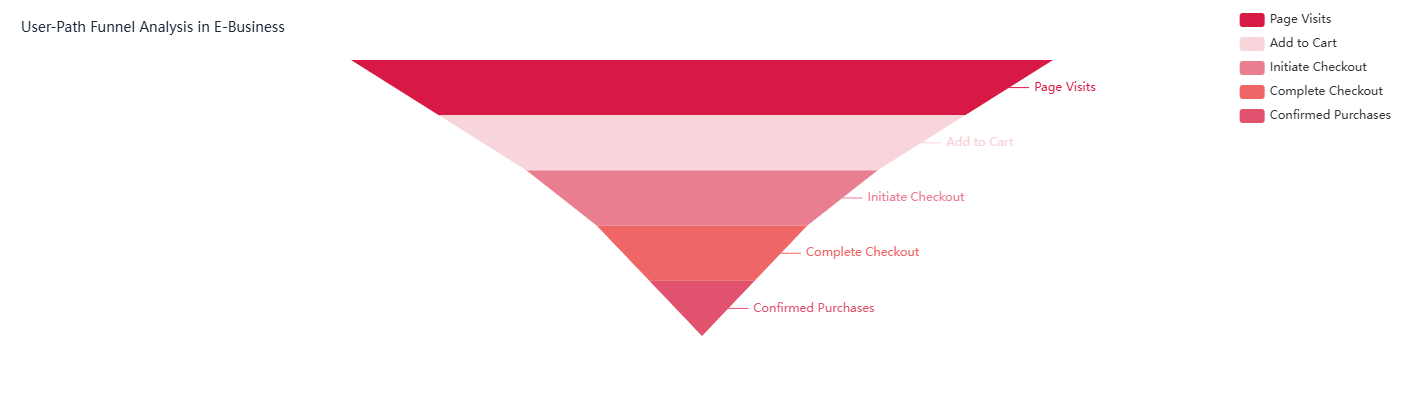
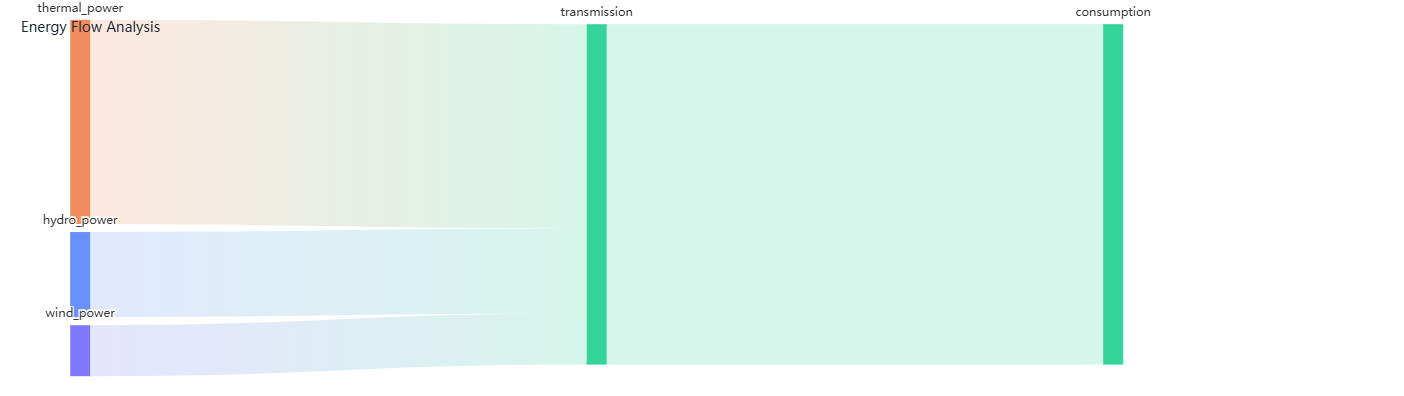
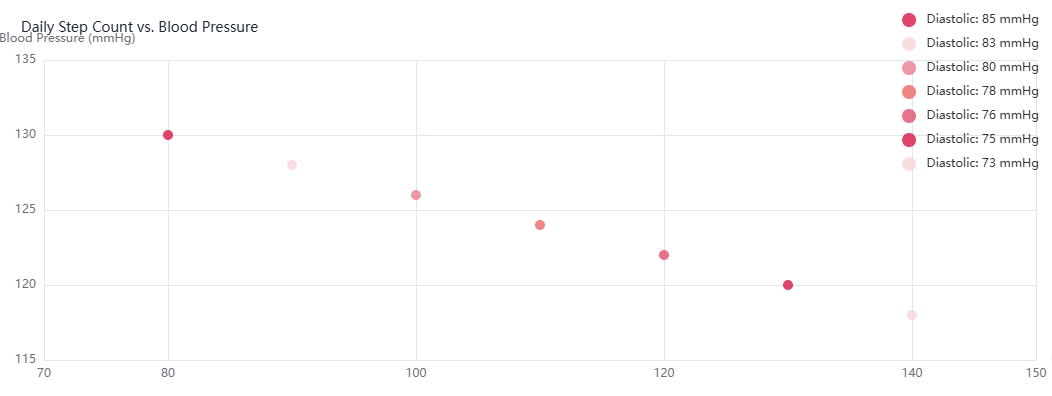
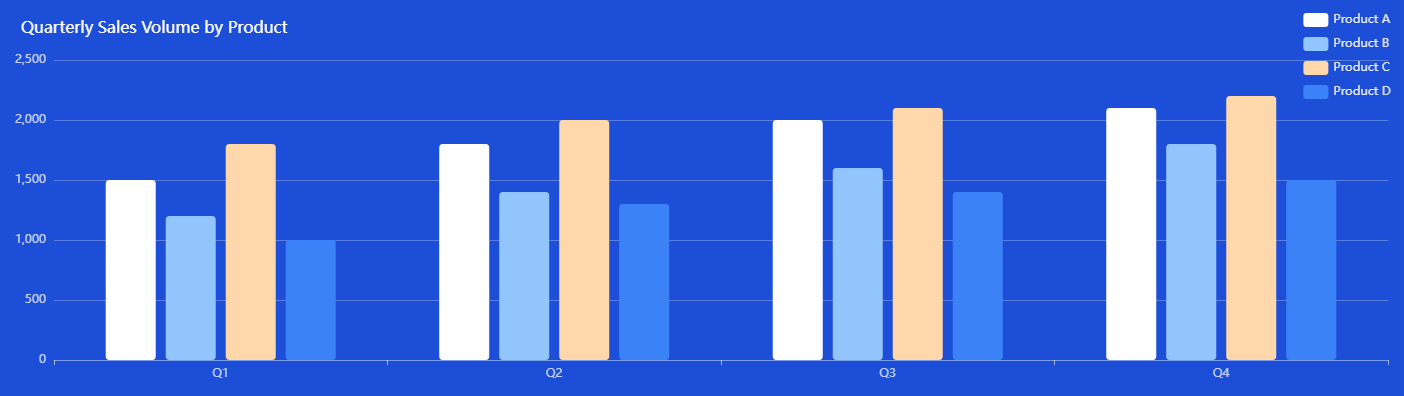
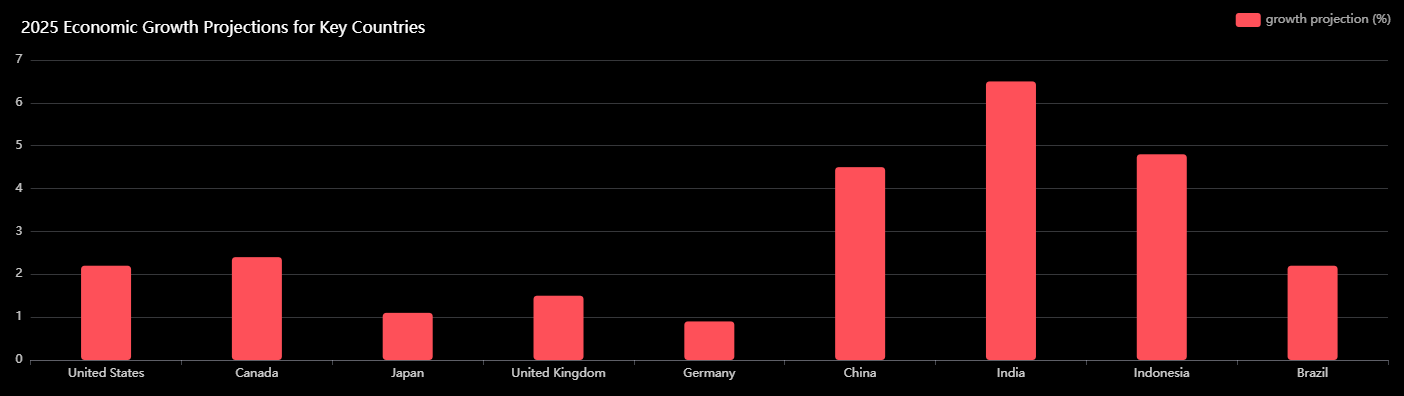
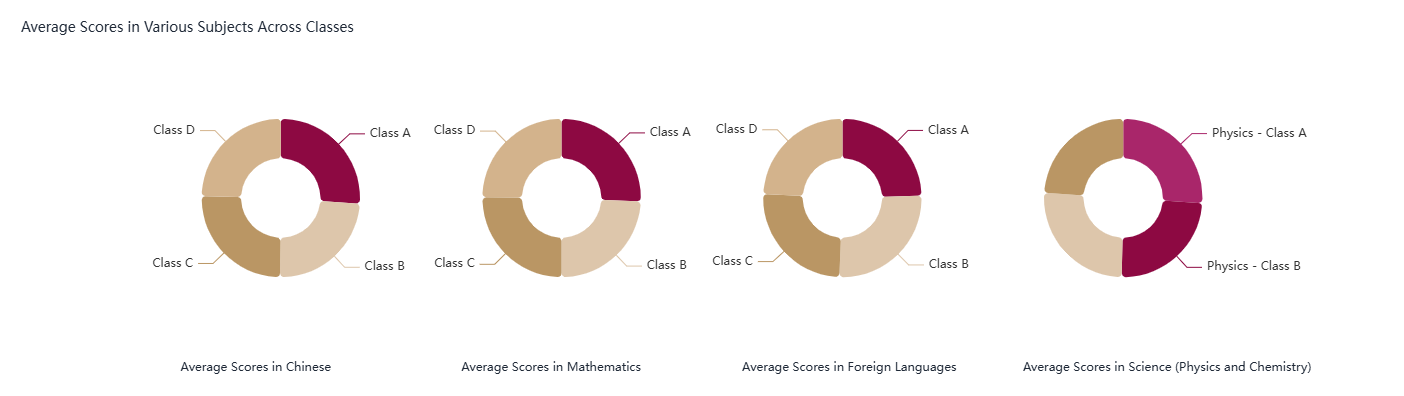
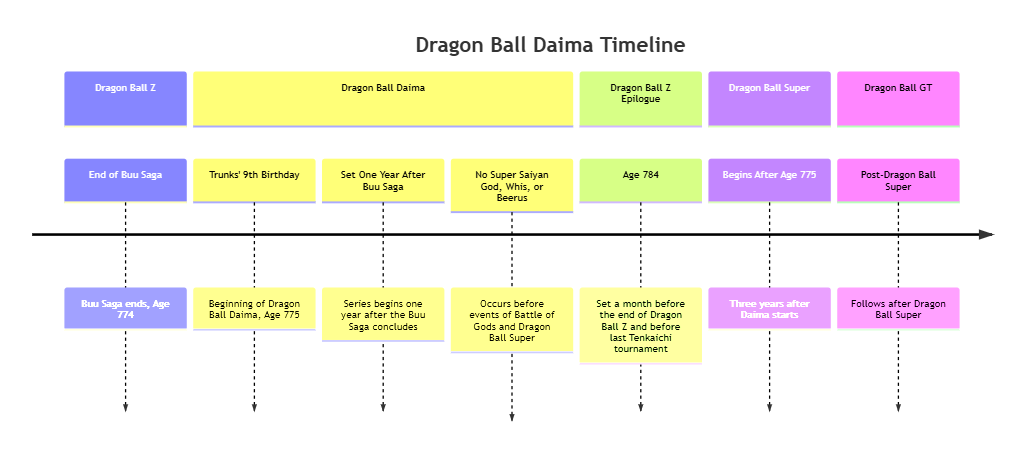
Description
Below is a bar chart - related description of "Western Europe's LNG Imports from the US and Russia (2018 - 2024)":
From 2018 to 2024, Western Europe's LNG imports from the US and Russia have shown the following characteristics and trends:
Overall Trends
From 2018 to 2022, Western Europe's LNG imports from the US and Russia generally exhibited growth trends. However, in 2023 and 2024, imports from the US slightly decreased while imports from Russia continued to rise.
US LNG Imports
* In 2018, imports began to increase gradually, with a growth rate of approximately [X]% compared to the previous year. By 2022, imports reached a peak, with the US accounting for [X]% of Western Europe's LNG imports. In 2023, imports slightly declined to [X]% but remained at a relatively high level. In 2024, they further decreased to [X]%.
Russian LNG Imports
* During the period from 2018 to 2021, imports showed a slow upward trend but accounted for a relatively small proportion of the total. In 2022, the import volume and share began to rise significantly. By 2024, Russia's share of Western Europe's LNG imports had increased to approximately [X]%, surpassing historical levels.
Reasons for Changes
* **From the US**: The increase in LNG imports from the US was primarily due to the expansion of US LNG export infrastructure, the growth of shale gas production, and the strengthening energy cooperation between Europe and the US. However, the decline in imports in 2023 and 2024 may be attributed to factors such as relatively high US LNG prices and adjustments in European energy demand.
* **From Russia**: The rise in LNG imports from Russia stemmed from the decline in pipeline gas exports from Russia to Europe, which led Europe to increase LNG imports from Russia to some extent to meet its natural gas needs. Additionally, Russia's efforts to diversify its energy export routes also contributed to the increase.
Overall Analysis
Despite fluctuations in the shares of US and Russian LNG imports in Western Europe, together they have become increasingly significant sources of LNG supply for the region. Their combined share rose from [X]% in 2018 to [X]% in 2024. This reflects the growing reliance of Western Europe on these two countries as LNG suppliers and highlights the dynamic nature of the global LNG market and the evolving energy landscape in Western Europe.