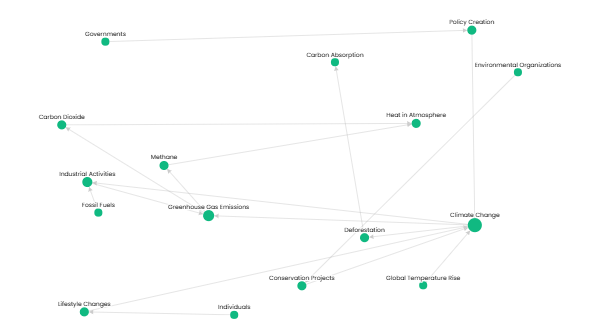
Climate change is driven by several factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and industrial activities. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane trap heat in the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise. Deforestation reduces the Earth's ability to absorb carbon dioxide, further accelerating climate change. Industrial activities, especially burning fossil fuels, contribute heavily to emissions. Governments, environmental organizations, and individuals take actions like policy creation, conservation projects, and lifestyle changes to mitigate climate change.
Entities and Types:
Climate Change — Concept
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — Concept
Deforestation — Concept
Industrial Activities — Concept
Carbon Dioxide — Chemical Compound
Methane — Chemical Compound
Global Temperature Rise — Effect
Governments — Organization
Environmental Organizations — Organization
Individuals — Person
Policy Creation — Action
Conservation Projects — Action
Lifestyle Changes — Action
Fossil Fuels — Resource
Relationships (ensuring all entities are connected):
Climate Change — caused by — Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Climate Change — accelerated by — Deforestation
Climate Change — accelerated by — Industrial Activities
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — contain — Carbon Dioxide
Greenhouse Gas Emissions — contain — Methane
Carbon Dioxide — traps — Heat in Atmosphere
Methane — traps — Heat in Atmosphere
Deforestation — reduces — Carbon Absorption
Fossil Fuels — burned in — Industrial Activities
Industrial Activities — emit — Greenhouse Gases
Global Temperature Rise — result of — Climate Change
Governments — implement — Policy Creation
Environmental Organizations — initiate — Conservation Projects
Individuals — adopt — Lifestyle Changes
Policy Creation — aims to mitigate — Climate Change
Conservation Projects — aim to mitigate — Climate Change
Lifestyle Changes — aim to mitigate — Climate Change
Description
## Concept Description
Climate change is a complex and multifaceted issue driven by a variety of factors that interact to alter the Earth's climate. These factors can be classified into several key categories:
### Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions are one of the primary drivers of climate change. Gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄) trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to a gradual increase in global temperatures. These gases are released through various human activities, including burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, and agricultural practices.
### Deforestation
Deforestation exacerbates climate change by reducing the Earth's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere and storing it in trees and soil. When forests are cleared for agriculture, logging, or development, this stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to higher greenhouse gas concentrations.
### Industrial Activities
Industrial activities, particularly those involving the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Factories, power plants, and transportation systems rely heavily on these fuels, releasing substantial amounts of CO₂ and other pollutants into the atmosphere.
## Relationships and Effects
### Heat Trapping
Carbon dioxide and methane are particularly effective at trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere. This heat - trapping property leads to an increase in global temperatures, resulting in a range of environmental impacts such as melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and more frequent extreme weather events.
### Reduced Carbon Absorption
Deforestation reduces the number of trees and plants that can absorb carbon dioxide. This decline in carbon absorption capacity means that more CO₂ remains in the atmosphere, further accelerating climate change.
### Fossil Fuel Burning
The burning of fossil fuels in industrial activities is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions contribute to the overall concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enhancing the greenhouse effect and driving global temperature rise.
### Global Temperature Rise
The cumulative effect of these factors results in a significant increase in global temperatures. This rise in temperature disrupts ecosystems, affects weather patterns, and poses threats to both environmental and human systems.
## Mitigation Actions
### Policy Creation
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating climate change through policy creation. By implementing regulations, incentives, and international agreements, governments can reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices.
### Conservation Projects
Environmental organizations initiate and manage conservation projects aimed at protecting forests and promoting reforestation. These projects help to preserve carbon sinks and enhance the Earth's ability to absorb CO₂.
### Lifestyle Changes
Individuals can contribute to climate change mitigation through lifestyle changes. Reducing energy consumption, using sustainable transportation, adopting plant - based diets, and minimizing waste are all actions that can help decrease an individual's carbon footprint.
## Conclusion
Climate change is a pressing issue that requires a multifaceted approach to address its root causes. By understanding the relationships between greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, industrial activities, and their impacts on global temperatures, stakeholders can develop effective strategies for mitigation. Governments, environmental organizations, and individuals all have important roles to play in creating a sustainable future and combating climate change.