Added on:
May 07, 2025
User Prompt
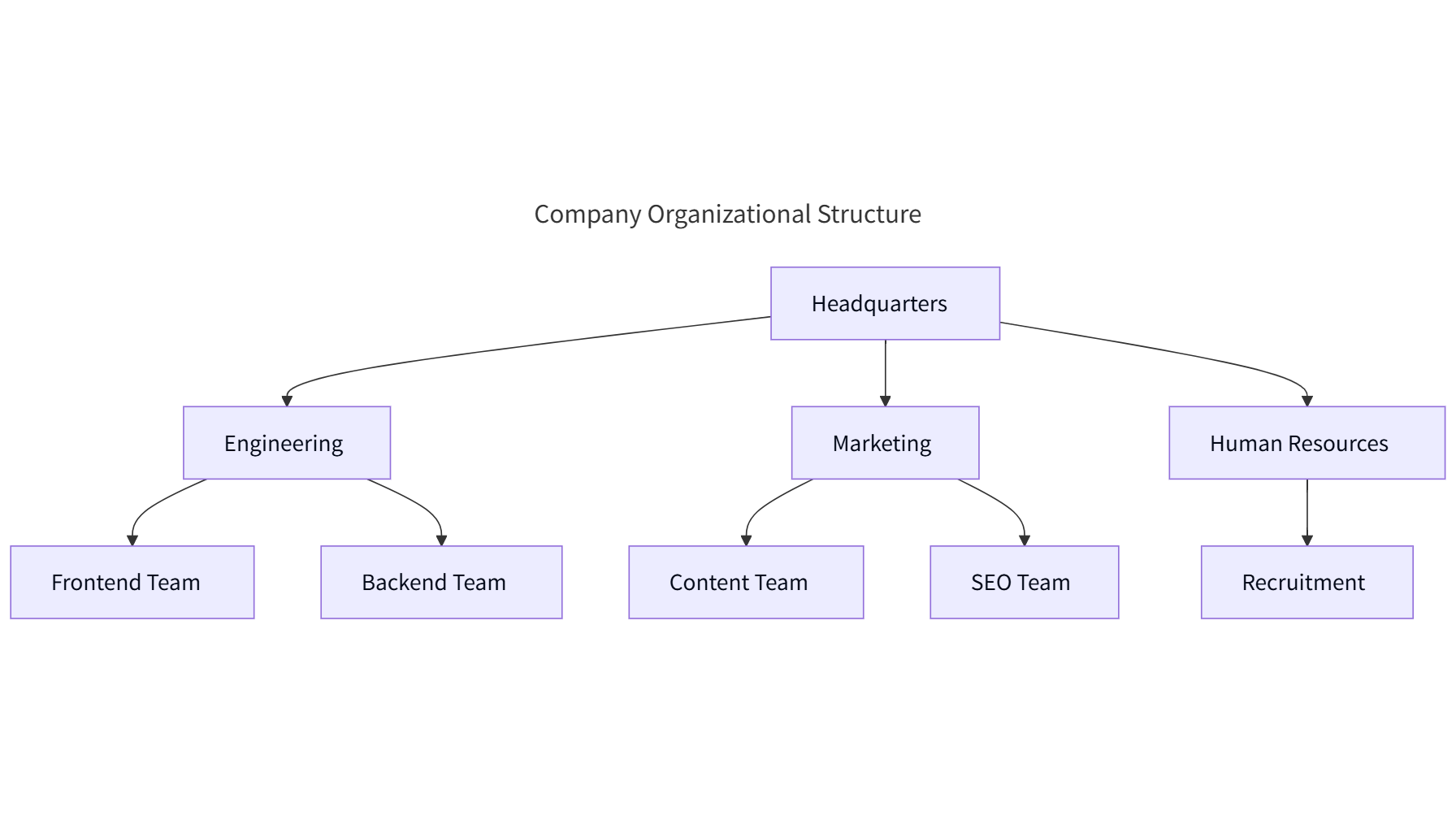
Class Diagram for E-commerce Platform: Modeling Product and Order Management Systems
Description
This class diagram illustrates the core components and relationships within an e-commerce platform’s product and order management systems, focusing on modular design for scalability and efficiency.
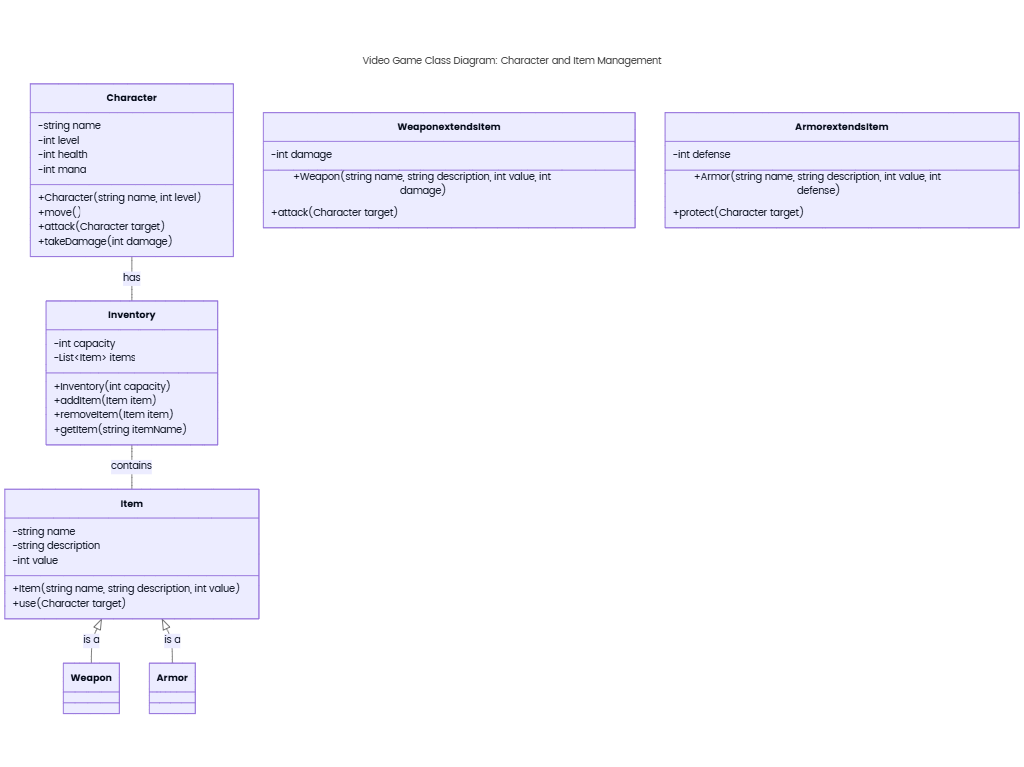
Core Classes & Attributes
- Product
- Attributes: Product ID (PK), Name, Description, Price, Stock Quantity, Category (e.g., Electronics, Apparel), Brand, Dimensions/Weight.
- Associations:
- Many-to-Many with OrderItem: A product can be included in multiple orders, and an order can contain multiple products.
- One-to-Many with ProductVariant: Manages variations (e.g., size, color) via subclasses like
ColorVariantorSizeVariant.
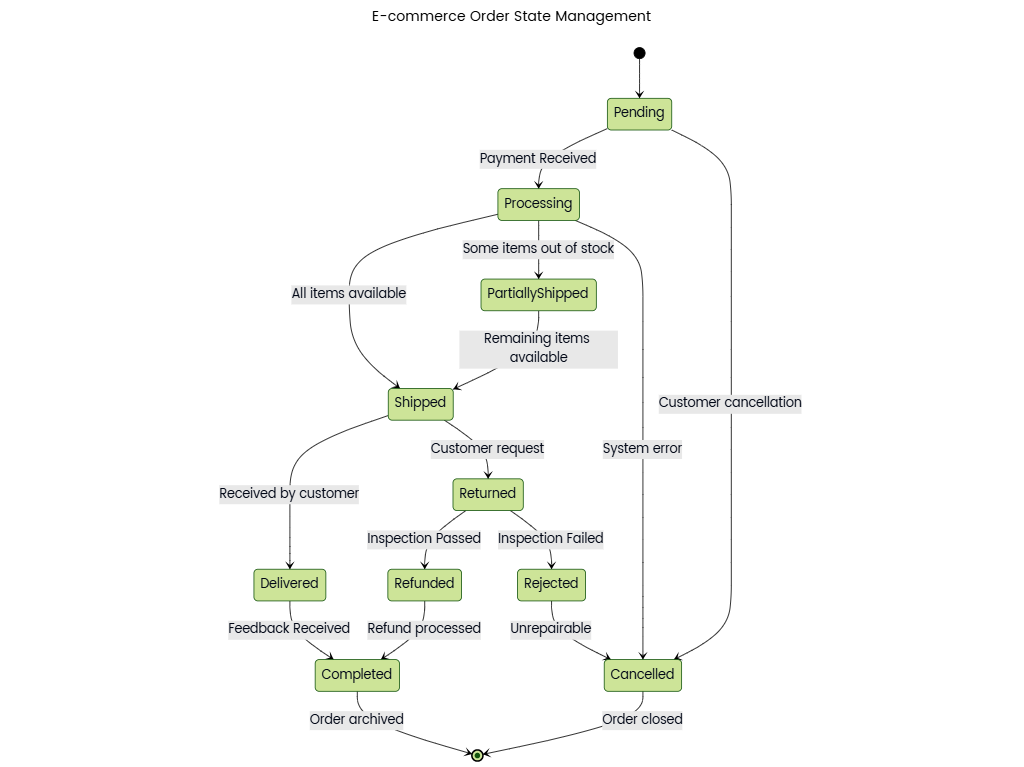
- Order
- Attributes: Order ID (PK), Order Date, Total Amount, Shipping Address, Billing Address, Status (Pending/Shipped/Delivered/Cancelled).
- Associations:
- One-to-Many with OrderItem: An order consists of multiple line items (e.g., 2 t-shirts and 1 phone case).
- One-to-One with Payment: Links to payment details (e.g., transaction ID, payment method).
- One-to-One with Customer: Identifies the buyer (Customer ID as FK).
- OrderItem
- Attributes: Order Item ID (PK), Quantity, Subtotal, Product ID (FK), Order ID (FK).
- Role: Represents individual products within an order, calculating subtotals and managing inventory deductions.
- Category
- Attributes: Category ID (PK), Category Name, Parent Category ID (for hierarchical structuring, e.g., "Electronics" → "Smartphones").
- Associations:
- One-to-Many with Product: Groups products into categories (e.g., "Smartphones" category contains multiple Product instances).
- InventoryManager
- Methods:
updateStock(Product, quantity),checkStockAvailability(Product). - Role: Manages real-time stock updates, preventing overselling and triggering reorder alerts.
- Methods:
- PricingStrategy
- Methods:
calculateDiscount(Product, orderTotal),applyTax(Subtotal). - Role: Implements dynamic pricing rules (e.g., seasonal discounts, bulk pricing) via strategies like
PercentageDiscountorFixedPriceOffer.
- Methods:
Key Relationships
- Product ↔ Category: Many-to-One
- A product belongs to one category (e.g., "iPhone 15" → "Smartphones" → "Electronics").
- Order ↔ OrderItem: Composition
- An
Orderis composed ofOrderIteminstances, meaning items cannot exist without an order.
- An
- Product ↔ ProductVariant: Inheritance/Composition
- Variants (e.g., "Red T-Shirt") inherit from
Productand add unique attributes (e.g., Color = Red, Size = M).
- Variants (e.g., "Red T-Shirt") inherit from
- Order ↔ Customer: Dependency
- Orders depend on
Customerdata (e.g., shipping address from theCustomerclass).
- Orders depend on
Business Logic & Workflow
- Order Placement:
- When a customer adds a
Productto their cart, anOrderItemis created with the selectedProductVariant(if applicable). InventoryManagerchecks stock availability viacheckStockAvailability(), reducingStock QuantityusingupdateStock()upon confirmation.
- When a customer adds a
- Pricing Calculation:
PricingStrategyapplies discounts (e.g., "10% off for orders over $100") and calculates tax, updating theOrder’sTotal Amount.
- Inventory Replenishment:
InventoryManagertriggers alerts whenStock Quantityfalls below a threshold (e.g., reordering products from suppliers).
Design Principles
- Modularity: Separate classes for
Product,Order, andInventoryManagerallow independent updates (e.g., adding new product types without altering order logic). - Scalability: Hierarchical
CategoryandProductVariantstructures support future expansions (e.g., new product lines or variant types). - Single Responsibility:
InventoryManagerandPricingStrategyfocus on specific tasks, improving maintainability.
This class diagram serves as a blueprint for developing a robust e-commerce system, ensuring seamless integration between product catalog management, order processing, and inventory control while accommodating future business growth.